Minimally Invasive Treatment of Vascular Diseases and Deformities/Malformations
Recanalizing/vasodilating procedures
- Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA)
- Endovascular prosthetic (stent) / endograft implantation (thoracic and abdominal aorta, visceral vessels, renal arteries, peripheral vessels, hemodialysis shunts)
- Local fibrinolysis, mechanical thrombectomy/atherectomy
Bildergalerie
(4 Bilder)
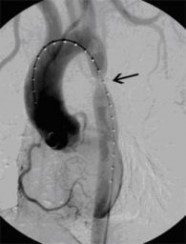 Aortenkoarktationsstenose vor Stentimplantation
(Bild 1 von 4)
Vorwärts »
Aortenkoarktationsstenose vor Stentimplantation
(Bild 1 von 4)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
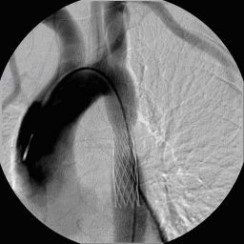
Aortenkoarktationsstenose nach Stentimplantation
(Bild 2 von 4)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Aortenkoarktationsstenose nach Stentimplantation
(Bild 2 von 4)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
Vor perkutaner transluminaler Angioplastie (PTA) der Unterschenkelgefäße
(Bild 3 von 4)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Vor perkutaner transluminaler Angioplastie (PTA) der Unterschenkelgefäße
(Bild 3 von 4)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
Nach perkutaner transluminaler Angioplastie (PTA) der Unterschenkelgefäße
(Bild 4 von 4)
« Zurück
Nach perkutaner transluminaler Angioplastie (PTA) der Unterschenkelgefäße
(Bild 4 von 4)
Occluding/vasoconstrictive procedures
- Embolization for gastrointestinal and/or postoperative bleeding
- Reduction of tumor vascularization preoperatively
- Embolization/occlusion for the elimination of vascular lesions, aneurysms, fistulas, and AV malformations (peripheral, pulmonary, renal)
- Sclerotherapy of varicose veins of the testicular/ovarian veins (for pelvic vein syndrome)
Bildergalerie
(5 Bilder)
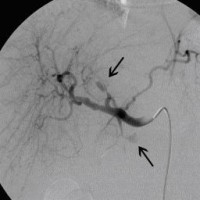 Postoperative abdominelle Blutungen bei chronischer Pankreatitis (Pfeile: Art. hepatica und Art. gastroduodenalis).
(Bild 1 von 5)
Vorwärts »
Postoperative abdominelle Blutungen bei chronischer Pankreatitis (Pfeile: Art. hepatica und Art. gastroduodenalis).
(Bild 1 von 5)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
Postoperative abdominelle Blutungen bei chronischer Pankreatitis vor Embolisation der Art. gastroduodenalis mittels Metallspiralen (Coils)
(Bild 2 von 5)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Postoperative abdominelle Blutungen bei chronischer Pankreatitis vor Embolisation der Art. gastroduodenalis mittels Metallspiralen (Coils)
(Bild 2 von 5)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
Postoperative abdominelle Blutungen bei chronischer Pankreatitis nach Embolisation der Art. gastroduodenalis mittels Metallspiralen (Coils)
(Bild 3 von 5)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Postoperative abdominelle Blutungen bei chronischer Pankreatitis nach Embolisation der Art. gastroduodenalis mittels Metallspiralen (Coils)
(Bild 3 von 5)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
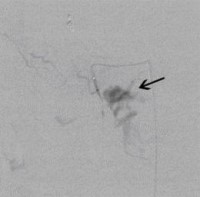
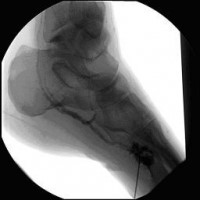
Perkutane Embolisation einer low-flow venösen Malformation (Gefäßmissbildung) der Fußsohle-1
(Bild 4 von 5)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Perkutane Embolisation einer low-flow venösen Malformation (Gefäßmissbildung) der Fußsohle-1
(Bild 4 von 5)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
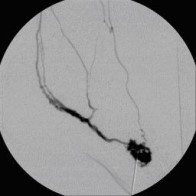
Perkutane Embolisation einer low-flow venösen Malformation (Gefäßmissbildung) der Fußsohle-2
(Bild 5 von 5)
« Zurück
Perkutane Embolisation einer low-flow venösen Malformation (Gefäßmissbildung) der Fußsohle-2
(Bild 5 von 5)
Special procedures
- Central venous port placement
- Permanent venous catheterization (Hickman, Shaldon, PICC-line = peripherally inserted central venous catheter)
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPSS) placement (for uncontrollable esophageal variceal bleeding, refractory ascites)
- Vena cava filter implantation (for recurrent/life-threatening pulmonary embolism due to deep vein thrombosis)
- Transjugular liver biopsy
- Percutaneous transvascular foreign body extraction (cath fragments, electrode remnants, etc.)
- Hormone blood sampling (parathyroid hormone, cortisol, ACTH, renin/angiotensin, insulin)
Bildergalerie
(4 Bilder)
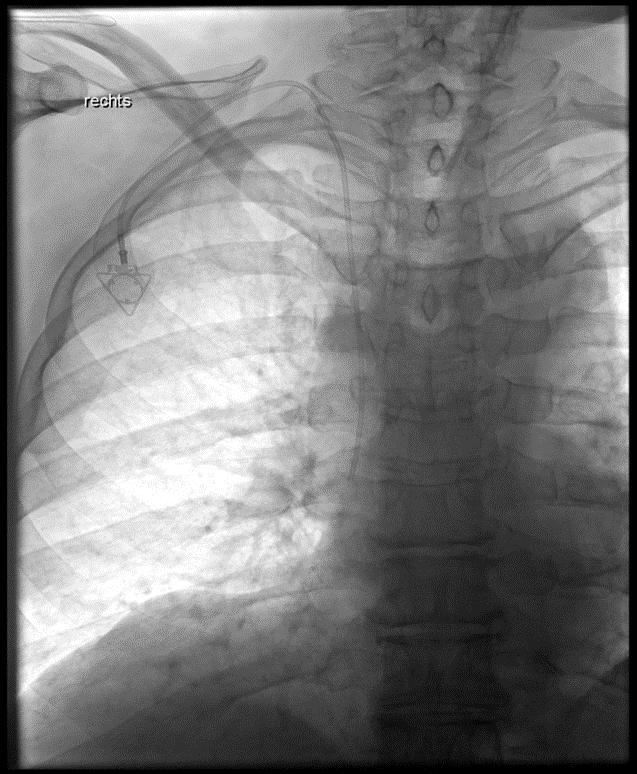 Implantation eines Port-Systems über die rechte innere Drosselvene (V. jugularis interna dextra)
(Bild 1 von 4)
Vorwärts »
Implantation eines Port-Systems über die rechte innere Drosselvene (V. jugularis interna dextra)
(Bild 1 von 4)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
Erfolgreiche Implantation eines transjugulären intrahepatischen portosystemischen Shunts (TIPSS) bei Leberzirrhose und refraktärem Aszites. Darstellung der Lebervenen
(Bild 2 von 4)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Erfolgreiche Implantation eines transjugulären intrahepatischen portosystemischen Shunts (TIPSS) bei Leberzirrhose und refraktärem Aszites. Darstellung der Lebervenen
(Bild 2 von 4)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
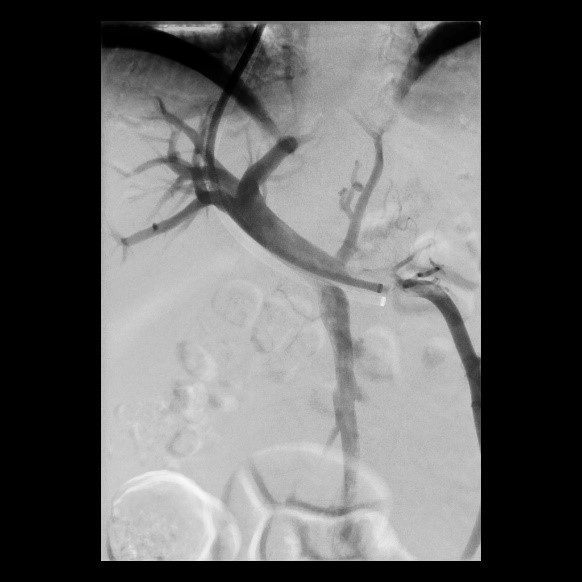
Erfolgreiche Implantation eines transjugulären intrahepatischen portosystemischen Shunts (TIPSS) bei Leberzirrhose und refraktärem Aszites. Transhepatische Punktion der Pfortader unter sonographischer Kontrolle
(Bild 3 von 4)
Vorwärts »
« Zurück
Erfolgreiche Implantation eines transjugulären intrahepatischen portosystemischen Shunts (TIPSS) bei Leberzirrhose und refraktärem Aszites. Transhepatische Punktion der Pfortader unter sonographischer Kontrolle
(Bild 3 von 4)
Vorwärts »
 « Zurück
Erfolgreiche Implantation eines transjugulären intrahepatischen portosystemischen Shunts (TIPSS) bei Leberzirrhose und refraktärem Aszites. Implantation eines Stentgrafts
(Bild 4 von 4)
« Zurück
Erfolgreiche Implantation eines transjugulären intrahepatischen portosystemischen Shunts (TIPSS) bei Leberzirrhose und refraktärem Aszites. Implantation eines Stentgrafts
(Bild 4 von 4)






