Perioperative Adaptions of Functional Brain Networks
The function of the brain is based on the integrity of neuronal functional networks. If the integrity is impaired, this manifests itself in neurological deficits.
In clinical practice, we encounter these failure modes on a daily basis. Currently, high-resolution contrast-enhanced and native structural, perfusion- and diffusion-based, and activity-related cranial MRI sequences are already acquired in routine imaging of our patients. Measurements of functional spontaneous activity have been lacking. Although these currently provide the only measurements for imaging functional networks.
rs-fMRI is a functional imaging modality that records BOLD signals at rest (Biswal et al. 1995). The frequency span is < 0.1 Hz in the low-frequency range. The measured spontaneous fluctuations are not to be classified as artifacts, but as the result of neuronal communication at rest (Cordes et al. 2001, Peltier et al. 2002).
In den letzten Jahren hat die Anwendung von rs-fMRT-Untersuchungen zunehmend Einzug in die Klinik erhalten. Dabei standen vor allem neurologische und psychiatrische Erkrankungen wie Autismus, ADHS, Schizophrenie, Alzheimer-Demenz oder der Morbus Parkinson im Mittelpunkt des Interesses (Fox and Greicius et al. 2010). So konnte beispielsweise bei Patienten mit ADHS-Syndrom eine Abnahme der funktionellen Konnektivität zwischen ACC (Anteriorer cingulärer Cortex) und PCC (Posteriorer cingulärer Cortex) beschrieben werden (Castellanos et al. 2008). Perspektivisch gilt es zu klären, ob rs-fMRT-Untersuchungen hier routinemäßig in der Diagnostik Anwendung finden könnten.
Ein weiteres Einsatzfeld stellt die Identifizierung neuronaler Netzwerke zum Zwecke der präoperativen OP-Planung in der Neurochirurgie dar. Gegenwärtig bietet vor allem die aufgabenbasierte fMRT die Möglichkeit Informationen über Struktur und Ausdehnung funktioneller Netzwerke zu erhalten (Petrella et al. 2006). Voraussetzung dafür ist jedoch ein kooperationsfähiger Patient. Dieser Umstand ist bei Bewusstlosen oder Kindern jedoch nicht gegeben. In diesen Fällen kann der Einsatz von rs-fMRT Verwendung finden (Nandakumar et al. 2019).
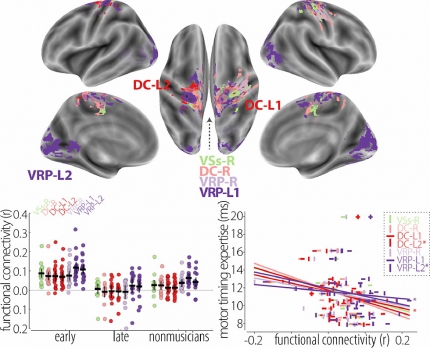
Fig. 3. Group differences in functional connectivity between early- and late-onset pianists. Early-onset pianists exhibited greater functional connectivity than late-onset pianists between the seed regions and a set of occipital and cortical sensorimotor areas, whereas functional connectivity to these areas was comparable between late-onset pianists and nonmusicians. The color of each patch indicates the seed region for which the area indicated greater functional connectivity. Barplot: functional connectivity across the seed regions (error bars indicate 2SE). Scatter plot indicates the correlation between functional connectivity and motor timing expertise (in ms; lower values correspond to greater expertise). Pianists who did not complete the scale playing task are omitted from the scatter plot. Analyses were performed in the volume but presented here on the cortical surface. VSi = ventral caudate/nucleus accumbens, VSs = ventral caudate, superior, DC = dorsal caudate, DCP = dorsocaudal putamen, DRP = dorsorostral putamen, VRP = ventrorostral putamen.





